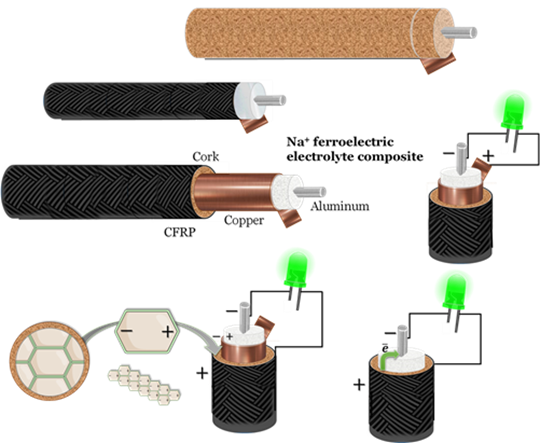
This invention introduces an innovative coaxial structural battery, revolutionizing the energy storage market. The device is a versatile energy harvesting/storage solution constituted by an internal element (electrode), surrounded by a dieletric material (electrolyte). The external shell holds the second electrode. This battery claims a remarkable theoretical capacity of 667 mAh/g , thanks to the ferroelectric electrolyte.
The development of energy storage technologies has seen significant advancements, particularly in the realm of coaxial structural batteries. A theoretical capacity of 667 mAh/g of the present coaxial battery stands in contrast to traditional lithium-ion batteries, which exhibit capacities ranging from 150 to 250 mAh/g. The use of cost-efficient materials such as aluminium and copper/carbon, combined with the ferroelectric eletrolyte, allow to have this advanced battery technology at a competitive price.
This coaxial structural battery is designed for versatility, making it ideal for various sectors, including mobility (e.g. electric vehicles), aerospace (e.g. planes) or construction (e.g. buildings, walls, roofs, floors). With its high energy density and stability, it offers a reliable and efficient power source. The battery design is free from hazardous materials and emissions (non-release of O2 and absence of Cobalt).
This coaxial structural battery stands at the forefront of energy storage technology, offering a unique combination of high performance, safety, and affordability. It's an ideal choice for businesses and consumers seeking efficient and sustainable energy solutions.
The coaxial cell is versatile as extends to various applications, including its potential integration into transistors, computers, photovoltaic cells, wind turbines, electric power transmission systems and other structures. Additionally, it demonstrates potential in transformers, power storage devices, and electric motors, showcasing its broad utility across different sectors of technology and industry.






